Table of Contents
The Domain 7: Security Operations of CISSP exam holds a total weightage of 13% in the exam.
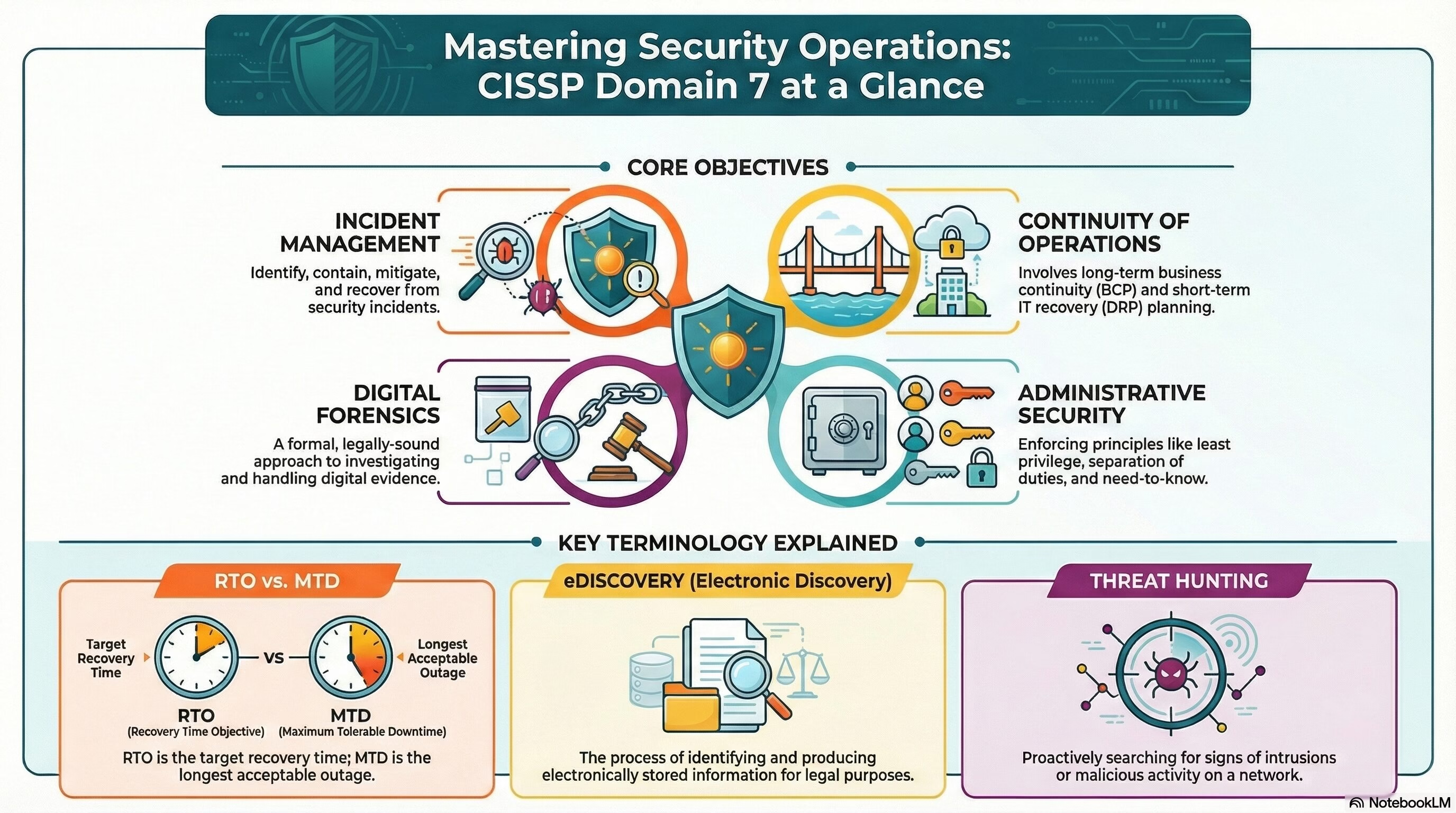
Below are the summaries of key objectives of Domain 7: Security Operations.
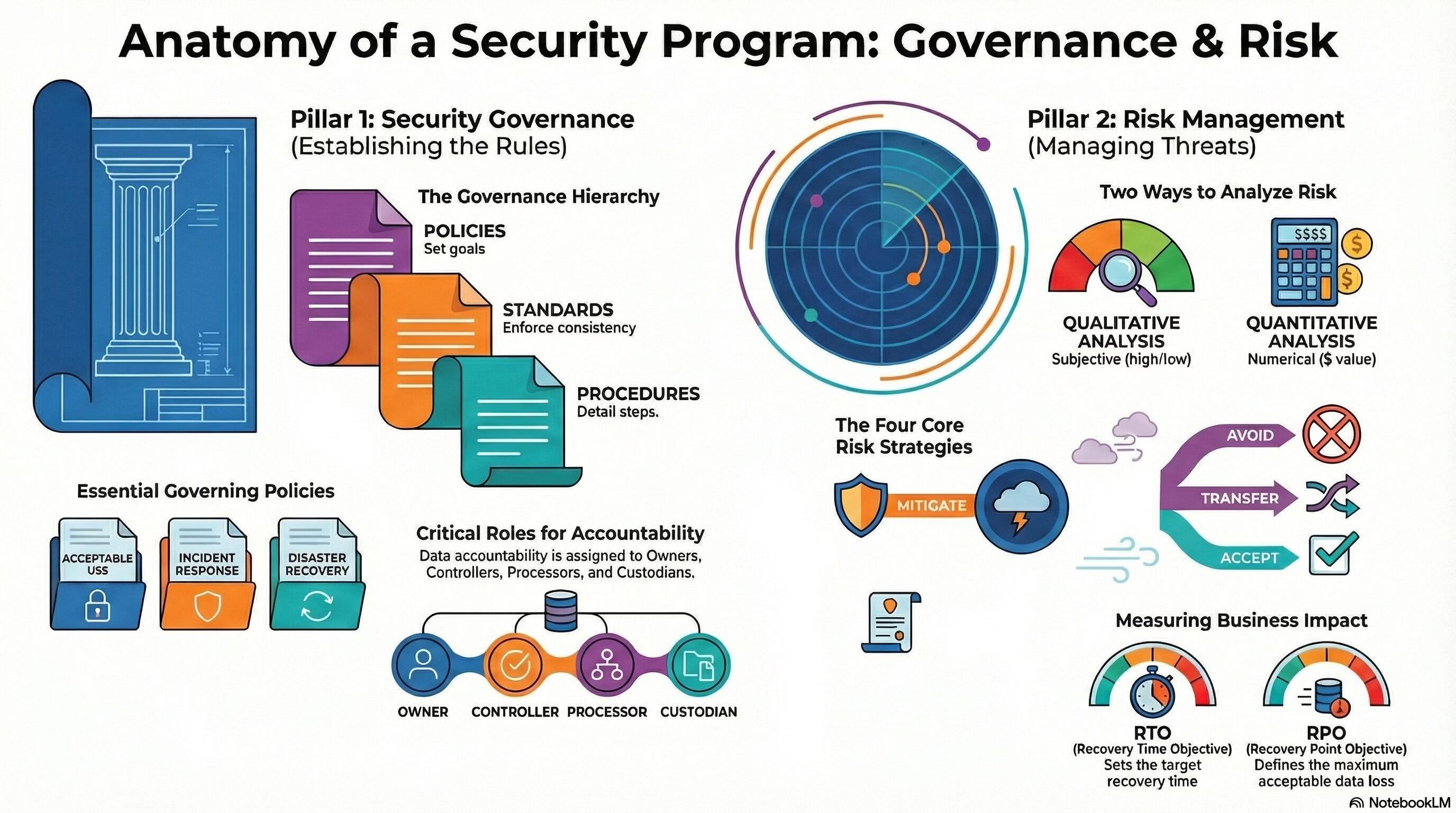
- Administrative Security: This involves ensuring that controls are in place to prevent people from either inadvertently or intentionally compromising the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of data or the systems and media holding that data. It includes concepts like least privilege, need to know, separation of duties, and rotation of duties.
- Forensics: This refers to the formal approach to dealing with investigations and evidence with special consideration of the legal aspects of this process. It includes digital forensics, network forensics, forensic software analysis, and electronic discovery (eDiscovery).
- Incident Management: This is about identifying, containing, and recovering from security incidents. It includes preparation, detection, response, mitigation, reporting, recovery, remediation, and lessons learned.
- Operational Preventive and Detective Controls: These are measures put in place to prevent security incidents and detect potential threats or vulnerabilities.
- Asset Management: This involves maintaining an inventory of all hardware and software assets within the organization, and ensuring they are properly managed and protected.
- Continuity of Operations: This is a plan to maintain operations during a disaster. It includes business continuity planning and disaster recovery planning.
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP): This is a long-term plan to ensure the continuity of business operations in the event of a disaster or other disruptive event.
- Disaster Recovery Planning (DRP): This is a short-term plan to recover from a disruptive event. It involves restoring IT infrastructure and systems to normal operations after a disaster.
Unique Terms and Definitions from Domain 7: Security Operations
- BCP/DRP – Business Continuity Plan/Disaster Recovery Plan. A set of policies and procedures that aim to ensure the continuity of critical business functions and minimize the impact of disruptive events.
- COOP – Continuity of Operations Plan. A plan that describes the procedures required to maintain operations during a disaster.
- RAID – Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. A method of using multiple disk drives to achieve greater data reliability, greater speed, or both.
- MTD – Maximum Tolerable Downtime. The maximum amount of time that a system or service can be unavailable before causing unacceptable harm to the organization.
- RTO – Recovery Time Objective. The target time for restoring a system or service after a disruption.
- WRT – Work Recovery Time. The time required to resume normal business operations after recovering from a disruption.
- Electronic Vaulting – The batch process of electronically transmitting data that is to be backed up on a routine, regularly scheduled time interval.
- Forensics – A formal approach to dealing with investigations and evidence with special consideration of the legal aspects of this process.
- eDiscovery – Electronic discovery. The process of identifying, preserving, collecting, processing, reviewing, and producing electronically stored information for legal purposes.
- Antiforensics – Techniques that make forensic investigation difficult or impossible.
- Software Escrow – A method of ensuring the availability of software source code by allowing a neutral third party to hold the code and provide it to the customer under certain conditions.
- Active-Active Cluster – A cluster configuration that involves multiple systems that are all online and actively processing traffic or data.
- Active-Passive Cluster – A cluster configuration that involves devices or systems that are already in place, configured, powered on, and ready to begin processing network traffic should a failure occur on the primary system.
- Digital forensics – a formal approach to dealing with investigations and evidence with special consideration of the legal aspects of this process.
- Antiforensics – techniques that make forensic investigation difficult or impossible, such as memory-resident malware, encryption, or data wiping.
- eDiscovery – the process of legal counsel gaining access to pertinent electronic information during the pre-trial discovery phase of civil legal proceedings.
- Threat hunting – the proactive search for indicators of intrusions or adversary activities within an organization’s network or systems, using threat intelligence as a guide.
- RAID – a method of using multiple disk drives to achieve greater data reliability, greater speed, or both, by using techniques such as mirroring, striping, or parity.
- MTD – Maximum Tolerable Downtime, the longest period of time that an organization can tolerate a system or service being unavailable without suffering unacceptable consequences.
- Software escrow – a contractual arrangement where a neutral third party holds the source code of a software product developed by a vendor for a customer, and releases it to the customer under certain conditions, such as the vendor going out of business or violating the terms of the agreement.
Multiple Choice Questions quiz
|
Flashcard quiz
|