Table of Contents
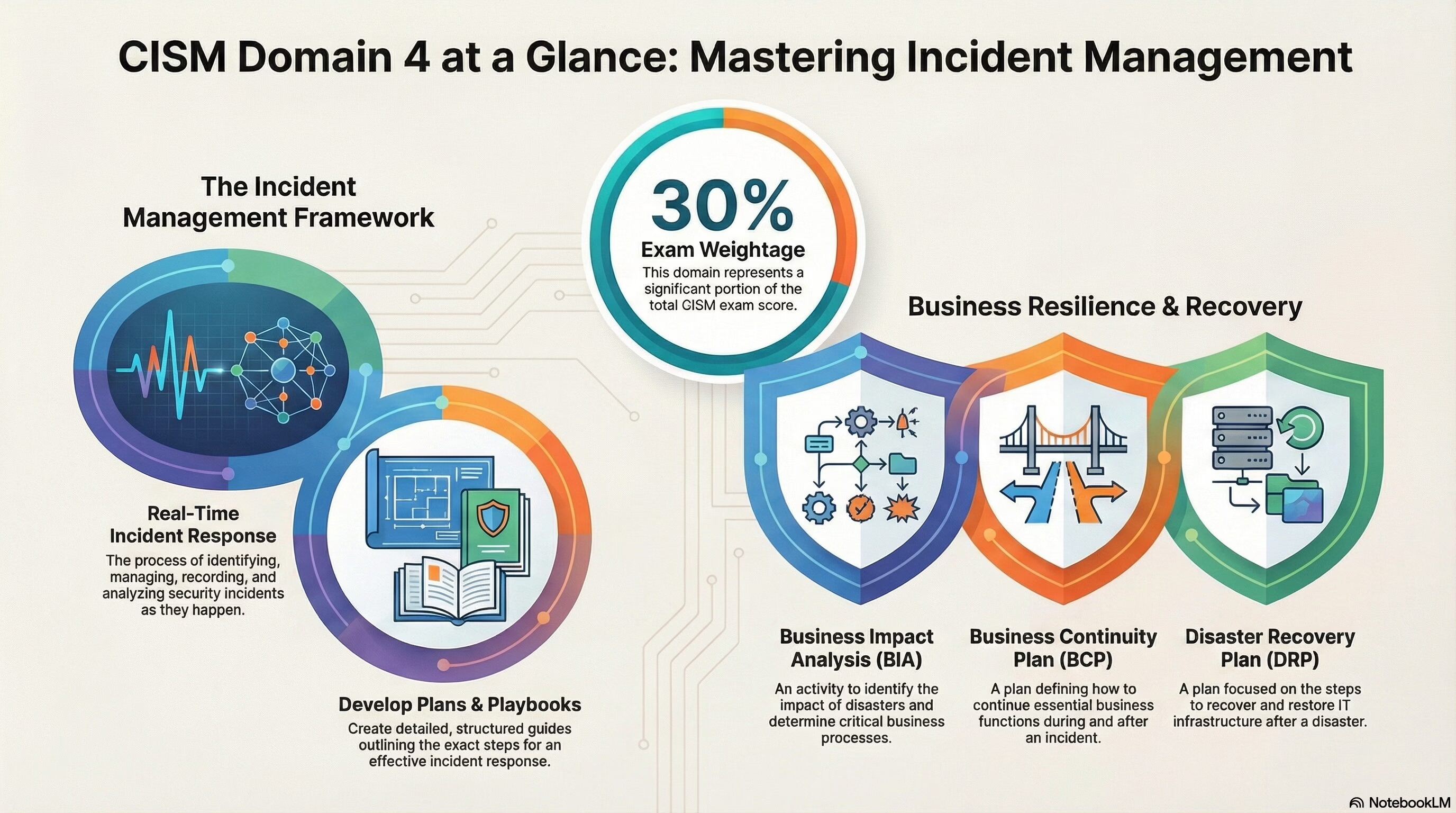
The Domain 4 – Incident Management of CISM exam holds a total weightage of 30% in the exam.
Below are the summaries of key objectives of Domain 4 – Incident Management.
The Information Security Incident Management domain is crucial for preparing candidates to effectively identify, respond to, and recover from security incidents, minimizing their impact on the organization’s operations and assets.
The Incident Management domain of the CISM certification encompasses the following key areas:
- Security Incident Response: This involves the process of identifying, managing, recording, and analyzing security threats or incidents in real-time, seeking to provide a robust and comprehensive view of any security issues within an IT infrastructure.
- Developing Security Incident Response Plans and Playbooks: Candidates are expected to be proficient in creating detailed response plans and playbooks that outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, ensuring a structured and effective response.
- Developing and Testing Business Continuity Plans: This includes the development and testing of plans to ensure that essential business functions can continue during and after a security incident.
- Developing and Testing Disaster Recovery Plans: Candidates should understand the process of creating and testing plans to recover and restore IT infrastructure and operations following a security incident or disaster.
Unique Terms and Definitions from Domain 4 – Incident Management
- Security incident: An event where the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information (or an information system) has been or is in danger of being compromised.
- Accept: A response to a threat where no course of action is taken.
- Acceptance criteria: The requirements and essential conditions that have to be achieved before a deliverable is accepted.
- Accrual: Work done for which payment is due but has not been made.
- Acquisition strategy: The establishment of the most appropriate means of procuring the component parts or services of a project.
- Activity: A task, job, operation or process consuming time and possibly other resources.
- Activity duration: The length of time that it takes to complete an activity.
- Activity ID: A unique code identifying each activity in a project.
- Activity network: A graphical representation of the logical relationships among the project activities. Also known as a network diagram.
- Activity status: The state of completion of an activity.
- Actual cost: The incurred costs that are charged to the project budget and for which payment has been made, or accrued.
- Actual cost of work performed (ACWP): The total costs actually incurred (paid or accrued) and recorded in accomplishing work performed during a given time period.
- Actual dates: The dates on which activities started and finished as opposed to planned or forecast dates.
- Actual expenditure: The costs that have been charged to the budget and for which payment has been made or accrued.
- Actual finish: The date on which an activity was completed.
- Actual progress: A measure of the work that has been completed in comparison with the baseline.
- Actual start: The date on which an activity was started.
- Agile: A set of principles and practices for delivering projects that emphasize flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction.
- APM: The Association for Project Management, a professional body for project management in the UK.
- APM Body of Knowledge: A collection of knowledge areas and terms that define the scope of project management as a profession, published by APM.
- Audit: A systematic and independent examination of project activities, documents, and processes to determine whether they conform to specified requirements.
- Baseline: A reference point or standard against which performance or progress can be assessed.
- Benefit: A measurable improvement resulting from an outcome that is perceived as an advantage by one or more stakeholders.
- Benefit management: The identification, definition, planning, tracking, and realization of benefits.
- Benefit realization: The process of ensuring that the benefits of a project are achieved and sustained after the project is completed.
- Bid: A proposal submitted by a prospective supplier in response to an invitation to tender.
- Bid evaluation: The process of assessing and comparing bids received from prospective suppliers, based on predefined criteria, such as price, quality, and technical capability.
- Budget: The approved estimate for a project or a work package.
- Business case: A document that provides the justification for initiating a project or task, based on the estimated costs, benefits, and risks.
- Business continuity plan (BCP): A plan that defines the methods that an organization will use to continue critical business operations after a disaster has occurred.
- Business impact analysis (BIA): An activity used to identify the impact of various disaster scenarios and to determine the most critical processes and systems in an organization.
- Business process: A set of interrelated activities that produce a specific output for a particular customer or stakeholder.
Multiple Choice Questions quiz
|
Flashcard quiz
|