Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction: Strategic Mandate and Guiding Principles
1.1 Setting the Vision for Information Systems Audit
The effective governance and management of information and technology are critical enablers of enterprise strategy. In this context, the Information Systems (IS) Audit function must evolve beyond a traditional compliance and control-testing role. This strategic plan outlines the multi-year vision for transforming the IS Audit function into a proactive and valued strategic partner. Our objective is to provide the Board and executive management with critical assurance and forward-looking insights, ensuring that the organization’s significant investments in technology are protected, optimized, and aligned with its core business objectives.
1.2 Vision and Mission Statement
Vision Statement To be a trusted and indispensable advisor to the enterprise, providing objective assurance and strategic insight that enables the confident and innovative use of information and technology to achieve market leadership and sustainable growth.
Mission Statement To conduct formal examinations of the enterprise’s information systems and processes, providing independent assurance that they are aligned with business objectives, compliant with relevant laws and governance criteria, and effectively managed to mitigate risk. We achieve this by systematically evaluating the design and operational effectiveness of internal controls that safeguard the organization’s information assets.
1.3 Guiding Principles and Professional Standards
The integrity and value of our work are predicated on an unwavering commitment to the highest professional standards. The following principles will guide all activities of the IS Audit function:
- Professional Ethics: We are unequivocally committed to upholding ISACA’s Code of Professional Ethics, which guides our professional and personal conduct to ensure the highest levels of integrity, objectivity, confidentiality, and competency.
- Adherence to Standards: All audit and assurance activities will be conducted in accordance with ISACA’s Information Technology Assurance Framework (ITAF). This includes adherence to all mandatory IS audit and assurance standards to ensure our work is consistent, reliable, and of the highest professional quality.
- Risk-Based Approach: Audit resources are finite and will be strategically allocated to areas of greatest significance to the enterprise. We will employ a formal risk-based audit planning methodology to prioritize our efforts on the systems and processes with the greatest potential impact on business objectives and strategic initiatives.
- Objective Assurance: Our primary deliverable is an independent and objective audit opinion. This opinion will be formed based on the collection and evaluation of sufficient, reliable, and relevant audit evidence, ensuring our conclusions are well-supported and actionable.
These principles form the bedrock of our function, ensuring our alignment with the broader enterprise governance and risk management structure.
2.0 Strategic Alignment with Enterprise Governance and Risk Management
2.1 Integrating IS Audit into the Governance Framework
Effective Information Technology (IT) governance is not a standalone discipline; it is an integral component of overall corporate governance. The IS Audit function plays a pivotal role in this ecosystem by providing independent assurance that the structures and processes governing IT are effective. This strategic plan ensures our activities are fully aligned with and supportive of the enterprise’s governance, risk, and compliance frameworks.
2.2 The IS Audit Role in Enterprise Governance of IT (EGIT)
The system by which our enterprise is directed and controlled is defined by its Corporate Governance framework. Within this, Enterprise Governance of Information and Technology (EGIT) is the critical process that ensures our IT strategies sustain and extend the enterprise’s overall strategies and objectives. The IS Audit function provides the board and executive management with assurance that this EGIT framework is effectively designed and operating. We independently verify that IT activities are aligned with business goals, conform to applicable laws and regulations, and that responsibilities are clearly assigned to manage risk effectively.
2.3 Supporting Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
The IS Audit function is a key partner in the organization’s Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework. We provide objective validation and assurance over the processes used to manage IT-related risks, ensuring they are identified, assessed, and treated in a manner consistent with the enterprise’s objectives.
- Risk Assessment Validation: We will independently review and validate the risk assessment processes used across the IT organization. This includes examining the methods for identifying threats and vulnerabilities, analyzing their potential impact, and evaluating the overall level of risk to the enterprise.
- Control Effectiveness Assurance: As part of the risk treatment process, management implements controls to modify risk. Our role is to provide independent assurance that these controls are appropriately designed and operating effectively to reduce risk to an acceptable level.
- Alignment with Risk Appetite: Our audit findings provide leadership with crucial insights into the operational reality of risk management. This helps them determine if the organization is operating within its defined risk appetite (the amount of risk it is willing to pursue) and risk tolerance (the readiness to bear risk after treatment).
Through these activities, we deliver the value and assurance necessary to execute the specific strategic pillars of this plan.
3.0 Core Strategic Pillars for Value Delivery
3.1 A Multi-Pillar Strategy for Comprehensive Assurance
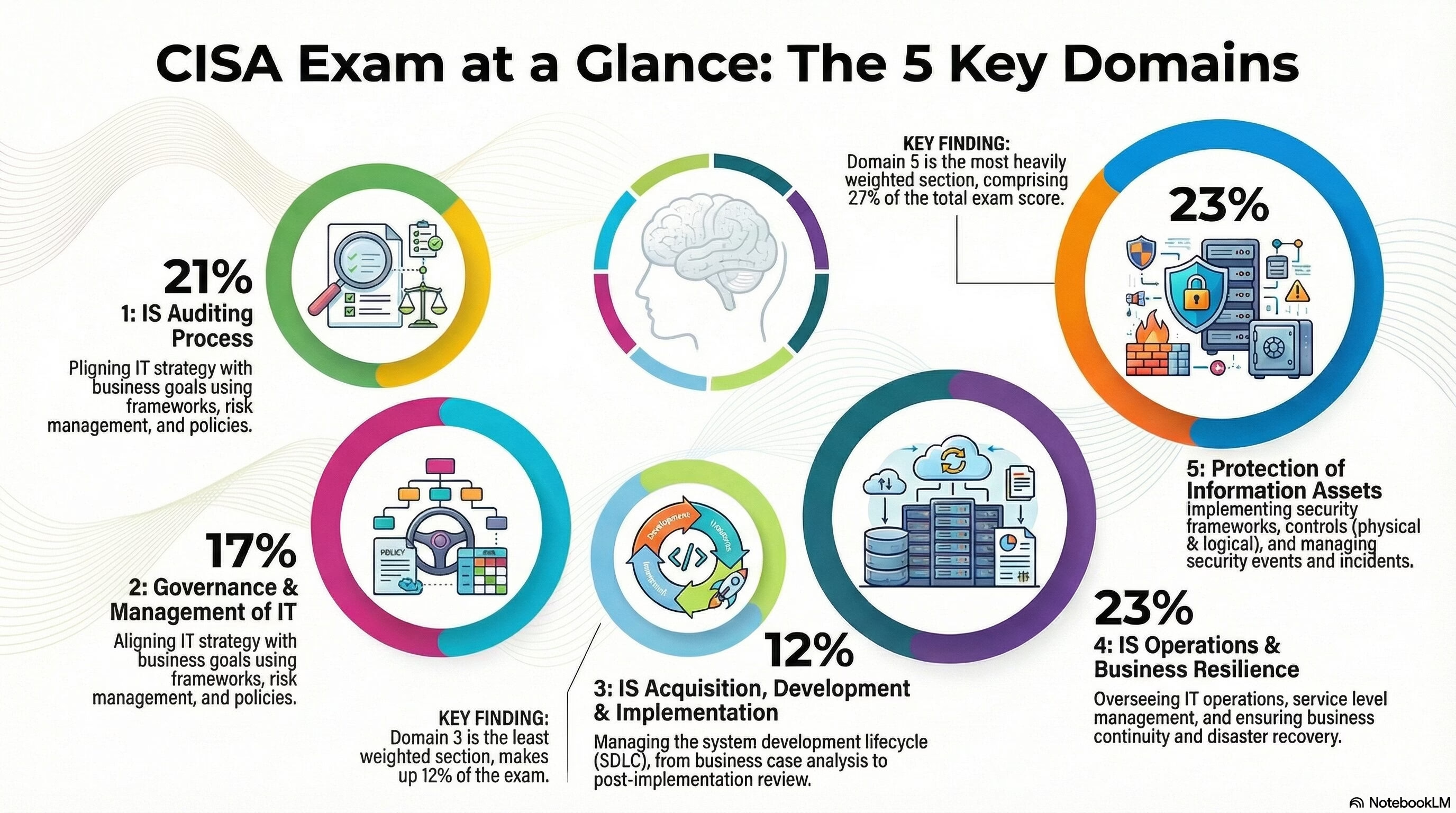
This multi-year plan is founded on four strategic pillars designed to provide comprehensive, risk-based audit coverage across the entire IT landscape. These pillars ensure that our efforts address foundational processes, strategic management, the technology lifecycle, and the critical protection of information assets, aligning our work with the best practices embodied in the CISA domains.
3.2 Pillar I: Foundational Audit Process Excellence
Excellence in our own processes is the foundation for providing credible assurance to the enterprise. We will standardize and continuously improve our audit methodology based on industry best practices.
- Standardized Audit Planning:
- Our function’s purpose, authority, and responsibility will be formally documented in an Audit Charter, approved by the highest level of management and the Board.
- Every engagement will be guided by a risk-based audit approach or strategy that clearly defines the audit scope and specific audit objectives to be achieved.
- Rigorous Audit Execution:
- Detailed audit programs will provide step-by-step procedures to ensure a consistent and thorough approach for every engagement.
- We will employ a variety of audit evidence collection techniques, including interviews, observation, and direct testing. A structured sampling methodology will be used where appropriate to draw statistically valid conclusions about entire populations.
- We will institutionalize the use of Data Analytics and Computer-Assisted Audit Techniques (CAATs) to analyze large datasets, identify anomalies, and gain deeper, data-driven insights that are not possible with traditional sampling.
- Impactful Communication and Follow-Up:
- We are committed to clear and concise Reporting and Communication Techniques, delivering our findings, conclusions, and recommendations in a formal Audit Report tailored to the relevant stakeholders.
- A formal audit follow-up process will be established to track management’s implementation of corrective actions, ensuring that identified risks are effectively remediated.
3.3 Pillar II: Governance and Strategic Alignment Assurance
We will provide assurance that the enterprise’s IT governance structures are effective and that IT strategy is aligned with business strategy.
- Framework Alignment: We will conduct audits against established IT governance and management frameworks, such as COBIT and ITIL, to assess the maturity of key processes and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Policy and Procedure Compliance: Our audits will test adherence to the established hierarchy of corporate Policies, IT Standards, and operational Procedures that govern the secure and efficient operation of technology.
- Performance Monitoring and Value Delivery: We will evaluate the effectiveness of IT Performance Monitoring and Reporting processes. This includes assessing the relevance and reliability of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) used to measure IT’s contribution to business goals.
- Third-Party Governance: We will provide assurance over the IT Service Provider Acquisition and Management process, ensuring that risks associated with vendors, suppliers, and service providers are effectively managed throughout the relationship lifecycle.
3.4 Pillar III: Technology Lifecycle and Operational Integrity
We will provide end-to-end assurance over the way technology solutions are acquired, developed, implemented, and operated.
- Acquisition and Development Assurance:
- Evaluate the Project Governance and Management processes for major IT initiatives to ensure they are managed effectively to deliver on-time and on-budget.
- Assess the rigor of the Business Case and Feasibility Analysis used to justify new system investments, ensuring they are based on sound assumptions.
- Audit the application of secure System Development Methodologies (SDLC) to verify that security and internal controls are identified and integrated during the design phase, not added as an afterthought.
- Implementation and Change Management Integrity:
- Review Testing Methodologies, from unit testing to user acceptance testing, to ensure system quality, functionality, and security before deployment.
- Audit the Change, Configuration, Release and Patch Management processes to ensure that modifications to production systems are controlled, tested, and authorized, thereby minimizing disruption and maintaining system stability.
- Operational Process Effectiveness:
- Assess the IT Asset Management program to ensure all hardware and software assets are identified, tracked, and appropriately secured throughout their lifecycle.
- Evaluate the Problem and Incident Management processes to ensure timely resolution of IT issues and effective root cause analysis to prevent recurrence.
- Review Database Management practices to provide assurance over the integrity, security, and performance of the organization’s critical data repositories.
3.5 Pillar IV: Information Asset Protection and Business Resilience
We will provide assurance over the controls and processes designed to protect the organization’s information assets and ensure operational resilience.
- Security Controls Framework: We will audit the design and effectiveness of the enterprise information security program against recognized frameworks, such as the ISO 27000 series or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, with a focus on ensuring the Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) of information assets.
- Access Control and Data Protection:
- Audits will assess the effectiveness of Identity and Access Management controls to ensure access to systems and data is granted on a need-to-know basis and revoked in a timely manner.
- Reviews will evaluate the enterprise Data Classification scheme and assess the consistent application of corresponding controls, such as Data Encryption, for sensitive data.
- Assessments will cover the effectiveness of Network and End-point Security controls, including Firewalls, Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS), and Antivirus software.
- Security Event Management and Incident Response:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of Security Monitoring Tools and Techniques, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, in detecting potential security incidents.
- Assess the organization’s Incident Response Management plan and capabilities through procedural reviews and participation in tabletop exercises.
- Review the organization’s procedures for Evidence Collection and Forensics to ensure they are sound and capable of supporting investigations.
- Business Resilience and Continuity:
- Assess the adequacy of the enterprise’s resilience framework, ensuring the Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is aligned with the Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and that technical Disaster Recovery Plans (DRP) are proven effective through testing. This includes auditing Data Backup, Storage and Restoration capabilities to confirm they can meet recovery objectives for the organization’s most critical information assets.
Successful execution of these four pillars is contingent upon building and maintaining the right capabilities within the IS Audit function itself.
4.0 Key Enablers for Strategic Execution
4.1 Building a High-Impact IS Audit Function
Executing this ambitious strategic plan requires a deliberate and sustained investment in the core capabilities of the IS Audit function. We will focus on enhancing our people, processes, and technology to deliver the high-impact assurance the enterprise requires.
4.2 Required Competencies and Technology
The following table outlines the key enablers essential for the successful execution of our strategy.
| Enabler | Strategic Imperative |
| Talent and Expertise | Develop and retain a team with the diverse skills of a professional IS auditor. This includes deep knowledge across critical areas such as project management, secure system development, security administration, and database management, as described across the CISA domains. |
| Advanced Audit Techniques | Fully integrate CAATs and Data Analytics into our core audit methodology. This will enable full-population testing, facilitate the identification of anomalies and trends, and provide deeper, data-driven insights into risks and control effectiveness. |
| Quality Assurance Program | Implement a formal Quality Assurance and Improvement process for the audit function. This program will include self-assessments and peer reviews to ensure our audit process remains effective, efficient, and consistently aligned with professional standards. |
These enablers will be developed and implemented according to a phased multi-year roadmap.
5.0 Multi-Year Roadmap and Performance Measurement
5.1 Phased Implementation for Maturity Growth
This strategic plan will be executed over three years in distinct phases. This approach allows for the progressive development of capabilities, moving the IS Audit function from a state of foundational compliance to one of strategic optimization and continuous assurance.
5.2 Three-Year Strategic Roadmap
The following roadmap outlines the key initiatives planned for each phase of our strategic transformation.
| Year 1: Foundational Capabilities | Year 2: Expanding Assurance | Year 3: Strategic Optimization |
| 1. Formalize the IS Audit Charter and establish governing procedures. | 1. Execute audits of IT governance frameworks (e.g., COBIT, ITIL). | 1. Implement continuous auditing techniques for key automated controls. |
| 2. Develop and implement a comprehensive risk assessment and risk-based audit planning process. | 2. Integrate audits into the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) for major projects. | 2. Conduct maturity model assessments (e.g., CMMI) of critical IT processes. |
| 3. Conduct baseline audits of critical IT General Controls, including change management and logical access. | 3. Launch a formal Data Analytics program using CAATs for key business processes. | 3. Perform audits of advanced security capabilities, including the governance of the penetration testing program and the effectiveness of incident response team exercises. |
| 4. Perform a baseline audit of the Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery plans. | 4. Deepen audits of cybersecurity controls, including network security and data encryption. | 4. Provide integrated assurance reports that connect IT risks and controls directly to strategic business objectives. |
5.3 Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The success of this strategic plan and the value delivered by the IS Audit function will be measured using the following Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Audit Plan Attainment: Percentage of the annual risk-based audit plan completed on schedule.
- Management Action Plan Implementation: Percentage of high-risk audit recommendations implemented by management within the agreed-upon timeframe.
- Audit Committee and Executive Feedback: Satisfaction ratings and qualitative feedback solicited annually from the Audit Committee and key executive stakeholders on the relevance, timeliness, and strategic value of audit insights.
- Audit Program Efficiency: Year-over-year reduction in audit cycle times and expansion of audit coverage achieved through the effective use of Data Analytics and CAATs.
Our progress against these goals will be governed by a clear oversight and communication framework.
6.0 Governance and Stakeholder Communication
6.1 Framework for Oversight and Reporting
A robust governance model is essential for ensuring the IS Audit function’s independence, objectivity, and impact. We will operate with transparent communication protocols and a clear reporting structure that reinforces our authority and accountability to the enterprise’s senior leadership and the Board.
6.2 Reporting Structure and Communication Plan
Our communication and reporting protocols will be structured to maximize transparency and ensure our work receives the appropriate level of attention and action.
- Authority and Independence: The IS Audit function’s authority, responsibility, and reporting lines will be formally documented in the Audit Charter. This charter will ensure direct and unrestricted communication channels to executive leadership and the Board of Directors or its designated audit committee.
- Formal Audit Reporting: All findings, conclusions, and recommendations will be communicated through a formal Audit Report. These reports will be distributed to relevant management stakeholders responsible for taking corrective action, as well as to senior leadership for oversight purposes.
- Continuous Engagement: We will implement a process for providing regular updates to leadership and the Board on the status of the annual audit plan, emerging technology risks, and the status of corrective actions tracked through our audit follow-up process.
This strategic plan represents our commitment to transforming the IS Audit function into a vital strategic partner. By executing this plan, we will provide the critical assurance and insight necessary for the enterprise to confidently navigate the complexities of the modern digital landscape, protect its assets, and achieve its most important business objectives.