Table of Contents
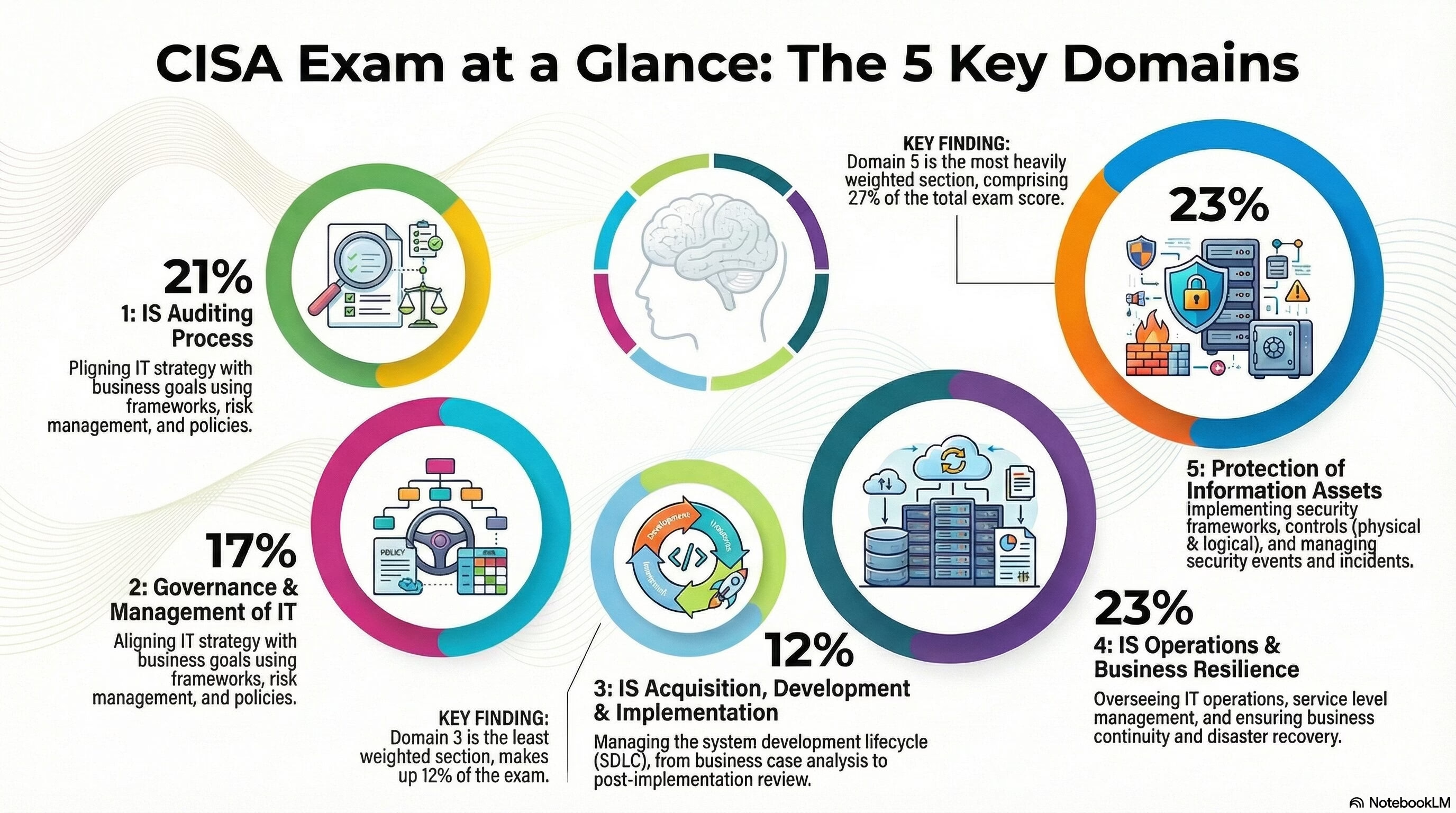
This study guide provides a review of key concepts from the five domains of the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) exam. It includes a short-answer quiz with an answer key, a set of essay questions for deeper analysis, and a comprehensive glossary of terms derived from the source materials.
Short-Answer Quiz
Instructions: Answer the following questions in two to three sentences each, based on the provided source context.
- What is the purpose of an audit charter, and how does it relate to the audit scope?
- Explain the difference between compliance testing and substantive testing as performed by an IS auditor.
- Describe the core function of Enterprise Governance of Information and Technology (EGIT) and its relationship to business objectives.
- How do policies, procedures, and guidelines differ from one another within an IT governance structure?
- Contrast the PERT and CPM project management techniques used in system development.
- What is the role of a post-implementation review in the information systems lifecycle?
- Explain the purpose of a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and what it is used to identify.
- Define IT asset management and list the key information that should be assigned to IT assets.
- What are the three key objectives of information security, and what is the common term for them?
- Differentiate between an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
——————————————————————————–
Answer Key
- An audit charter is a formal document that defines the purpose, authority, and responsibility of the IS audit function. It provides the foundation for the audit’s mandate, while the audit scope defines the specific systems, functions, or organizational units that will be included in a particular audit review.
- Compliance testing verifies that control procedures are being performed in accordance with established policies and standards. In contrast, substantive testing is used to verify the accuracy and completeness of data and transactions through detailed or analytical tests.
- EGIT is the process of establishing a framework and management structure to ensure that information and technology strategies align with and support business objectives. It also ensures that these strategies are consistent with applicable laws and regulations and that responsibilities are clearly assigned to manage risk.
- Policies are high-level statements of management intent that support business strategy. Procedures are detailed, step-by-step instructions for performing a specific task. Guidelines are helpful, non-mandatory information, such as examples or clarifications, that aid in executing the procedures.
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) is a project management technique that uses three different time estimates for each activity to determine a project’s expected completion time. CPM (Critical Path Method) identifies the longest sequence of dependent tasks (the critical path) to determine the shortest possible completion time for the entire project.
- A post-implementation review is conducted after a new system is in place to evaluate the overall success of the project. Its purpose is to identify areas for improvement and to ensure that the project met its original goals and aligned with business objectives.
- A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a technique used to identify and prioritize an organization’s critical business processes. It assesses the potential impact that disruptions to these processes would have on the organization, forming a basis for business resilience planning.
- IT asset management is the process of identifying, inventorying, managing, and protecting all IT assets, including hardware, software, and data. Key information assigned to assets includes owners, custodians, values, locations, security classifications, and potential loss implications.
- The three key objectives of information security are confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This set of principles is commonly referred to as the CIA triad.
- An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a tool that monitors network or system activities for malicious behavior and generates alerts. An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) also monitors for malicious activity but can actively block or prevent the detected incidents from occurring.
——————————————————————————–
Essay Questions
Instructions: The following questions are designed for long-form essay answers. Use the information provided in the source context to construct a comprehensive response that synthesizes concepts across different domains.
- Describe the complete lifecycle of an IS audit, from initial planning to follow-up. Incorporate key concepts from Domain 1, such as risk-based planning, evidence collection, reporting, and the role of ISACA standards.
- Explain how IT Governance frameworks (e.g., COBIT, ITIL) as described in Domain 2 provide the structure for managing IT resources, monitoring performance, and ensuring the protection of information assets (Domain 5).
- Discuss the critical role of an IS auditor throughout the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) as outlined in Domain 3. How do the principles of control identification, testing methodologies, and post-implementation review contribute to a successful project?
- Analyze the relationship between Information Systems Operations (Domain 4, Part A) and Business Resilience (Domain 4, Part B). How do effective problem management, change control, and systems performance management contribute to an organization’s ability to withstand and recover from disruptions?
- Using concepts from Domain 5, construct a multi-layered information security strategy for a modern enterprise. Your answer should address physical controls, identity and access management, network security, data encryption, and security event management.
——————————————————————————–
Glossary of Key Terms
| Term | Definition |
| 4GL (Fourth-generation Language) | A high-level, nonprocedural, portable and user-friendly programming language that allows developers to focus on the business functionality and logic rather than the technical details of the system. |
| ActiveX | A software framework and technology that allows components to interact and share information across different applications and platforms, such as web browsers, Microsoft Office and Windows OS. |
| AI (Artificial Intelligence) | The branch of computer science that deals with creating systems or programs that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, decision making or natural language processing. |
| Antivirus software | A program that can prevent, detect and remove malware infections on a computer system. |
| Asymmetric encryption | A type of encryption that uses a pair of keys, one for encryption and one for decryption, also known as public key encryption or dual key encryption. |
| Attribute sampling | A sampling technique used to estimate the rate of occurrence of a specific quality or attribute in a population, such as the presence or absence of a control procedure. |
| Audit approach or strategy | The methodology used to conduct the audit, such as risk-based, control-based or substantive testing. |
| Audit charter | A document that defines the purpose, authority and responsibility of the IS audit function. |
| Audit evidence | The information obtained by an IS auditor during the audit process to support the audit opinion and conclusions. |
| Audit follow-up | The process of monitoring and ensuring that agreed-upon recommendations or corrective actions have been implemented by management. |
| Audit objective | The purpose of the audit, such as to determine whether a system is secure, reliable, compliant or effective. |
| Audit opinion | The formal expression of the IS auditor’s findings and conclusions on the audit subject matter. |
| Audit program | A step-by-step set of audit procedures and instructions that should be performed to complete an audit. |
| Audit report | The written communication of the IS auditor’s findings and recommendations to the intended recipients and users of the audit. |
| Audit risk | The risk that an IS auditor may express an inappropriate audit opinion when the audit subject matter is materially misstated. |
| Audit scope | The specific systems, function or unit of the organization to be included in the audit review. |
| Biometric access control | A logical access control technique that uses a person’s unique physical or behavioral characteristics, such as fingerprint, iris, voice or signature, to verify their identity. |
| BPR (Business Process Reengineering) | The radical redesign and improvement of the existing business processes, workflows and systems of an organization to achieve significant gains in performance, quality, customer satisfaction and profitability. |
| Business intelligence (BI) | A broad field of IT that encompasses the collection and analysis of information to assist decision-making and assess organizational performance. |
| Business process | An interrelated set of cross-functional activities or events that result in the delivery of a specific product or service to a customer. |
| CAATs (Computer-assisted audit techniques) | The use of software tools and utilities to perform audit tests or procedures on data or systems. |
| Card key | A physical access control technique that uses a plastic card with a magnetic strip or a chip containing encoded data to provide access to restricted or secure locations. |
| CASE (Computer-aided Software Engineering) | The use of automated tools to support the software development process, such as requirements analysis, design, coding, testing, documentation and maintenance. |
| Central processing unit (CPU) | The main component of a computer that performs arithmetic and logical operations, controls the execution of instructions and communicates with other devices. |
| Cloud computing | A model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. |
| Cloud deployment models | The four types of cloud environments, namely public cloud, private cloud, community cloud and hybrid cloud. |
| Cloud service models | The three types of services offered by cloud providers, namely software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). |
| COBIT | A framework developed by ISACA to help enterprises optimize the value of information assets, by providing guidance on governance and management of information and technology. |
| COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language) | A procedural, imperative and compiled programming language that is designed for business applications and runs on a variety of platforms, such as mainframes, minicomputers and microcomputers. |
| Code of Professional Ethics | A set of principles that guides the professional and personal conduct of ISACA members and certification holders. |
| Compliance testing | The process of verifying that control procedures are being performed in accordance with policies and standards. |
| Conceptual schema | A data schema that describes the overall structure and meaning of the data for the entire organization, independent of any physical or logical implementation. A conceptual schema defines the entities, attributes and relationships in an entity-relationship diagram (ERD). |
| Confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA) | The three key objectives of information security, also known as the CIA triad. |
| Control | A measure that is modifying risk. |
| Control framework | A set of criteria, standards or best practices that can be used to assess and improve the internal control environment of an organization. (From Domain 1) / A collection of best practices, guidelines and methodologies for designing, implementing and assessing controls in an organization. (From Domain 5) |
| Control objective | A statement of the desired result or purpose to be achieved by implementing control procedures in a particular process. |
| Control procedure | A specific action or set of actions that are performed to achieve a control objective. (From Domain 1) / A policy, standard or rule that reduces the impact or likelihood of an adverse event. (From Domain 2) |
| Control self-assessment (CSA) | A technique that involves the participation of operational management and staff in assessing the effectiveness of controls within their own area of responsibility. |
| Control testing | The process of verifying the effectiveness and efficiency of control procedures through compliance or substantive tests. |
| Corporate governance | The system by which enterprises are directed and controlled, involving a set of relationships among a company’s management, its board, its shareholders and other stakeholders. |
| CPM (Critical Path Method) | A project management technique that identifies the sequence of activities that produces the longest path through a project and determines the shortest possible completion time of the project. |
| CPU (Central Processing Unit) | The main component of a computer system that executes the instructions of a program and performs the arithmetic and logical operations. |
| CSF (Critical Success Factor) | A factor that is essential for achieving a desired outcome or objective of a project, program or organization. |
| Data architecture | A framework that consists of the enterprise data flow architecture (EDFA) and a logical data architecture, which define and organize the data entities and how they relate and flow within and between the various layers of the data environment. |
| Data custodian | A person who is responsible for storing and safeguarding the data and providing access to authorized users. |
| Data governance | A process that involves determining which BI initiatives to fund, what priority to assign to initiatives and how to measure their return on investment (ROI), as well as establishing standard definitions for data, business rules and metrics, identifying approved data sources, and establishing standards for data reconciliation and balancing. |
| Data owner | A person who is accountable for the security and use of a specific set of information assets, such as data or applications. |
| Data schema | A representation of the logical organization of data in a database. A data schema defines the data elements, their attributes, their domains and their relationships. |
| Data user | A person who accesses and uses the data for legitimate business purposes. |
| Database administrator (DBA) | A person who defines and maintains the data structures in the corporate database system, understanding the organization and user data and data relationship requirements, and ensuring the security and integrity of the data. |
| Database management system (DBMS) | System software that manages the creation, storage, retrieval, manipulation and security of data in a database. |
| Database structure | The way that data are organized and stored in a database, based on a data model. |
| DFD (Data Flow Diagram) | A graphical representation of the flow of data and the processing steps of a system or a process, using symbols such as circles, arrows, rectangles and parallel lines. |
| Digital envelope | A technique that combines symmetric and asymmetric encryption to securely transmit data and a secret key, by encrypting the data with the secret key and then encrypting the secret key with the recipient’s public key. |
| Digital signature | A technique that uses asymmetric encryption to verify the authenticity and integrity of a message or document by applying the sender’s private key to a digest of the message or document. |
| EAL (Evaluation Assurance Level) | A numerical rating that indicates the level of confidence in the security functionality and assurance of an IT product or system, based on a standardized criteria and evaluation process. |
| EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) | The exchange of structured data between computer systems according to agreed standards. |
| EJB (Enterprise Java Beans) | A server-side component model for developing and deploying distributed, scalable, secure and transactional business applications on Java platforms. |
| Encryption | The process of converting a plaintext message into a ciphertext that cannot be understood without converting it back via decryption using a key. |
| Encryption algorithm | A mathematical function that encrypts and decrypts data using a key. |
| Encryption key | A piece of information that is used by the encryption algorithm to make the encryption or decryption process unique. |
| Enterprise governance of information and technology (EGIT) | The process of establishing and maintaining a framework and supporting management structure and processes to provide assurance that information and technology strategies are aligned with and support business objectives, are consistent with applicable laws and regulations, and provide assignment of responsibility, all in an effort to manage risk. |
| ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram) | A graphical representation of a system’s data and how they interrelate, using entities, attributes, keys and relationships. An ERD can be used as a logical data model or a physical data model. |
| ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) | A large-scale, integrated software system that supports the core business processes and functions of an organization, such as accounting, finance, human resources, manufacturing, sales and marketing. |
| Expert system | A type of AI system that uses a knowledge base and an inference engine to emulate the reasoning and judgment of a human expert in a specific domain. |
| External schema | A data schema that describes the structure and meaning of the data for a specific user or application, based on the conceptual schema. |
| Firewall | A device or software that monitors and controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules, acting as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks. |
| Guidelines | Information that will be helpful in executing the procedures, such as clarification of policies and standards, dependencies, suggestions and examples, narrative clarifying the procedures, background information and tools that can be used. |
| Hardware maintenance program | A program that documents the performance of routine cleaning and servicing of hardware to ensure proper operation and availability. |
| Hardware monitoring procedures | Procedures and reports that measure and evaluate the use and performance of hardware resources, such as availability, errors, utilization and capacity. |
| Hardware platforms | The physical devices and equipment that support the operation and use of information systems, such as servers, workstations, routers, switches, printers and scanners. |
| Hardware reviews | Reviews that assess the hardware acquisition plan, the hardware acquisition process, the IT asset management, the capacity management and monitoring, and the preventive maintenance schedule. |
| Hierarchical database model | A database model that organizes data in a tree-like structure, using parent-child relationships. |
| Honeypot | A decoy system or network that is designed to attract and trap attackers, diverting them from the real targets and collecting information about their activities and techniques. |
| HTML (HyperText Markup Language) | A standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications, using tags, elements and attributes to define the structure and content of the document. |
| I/O (Input/output) components | Devices that allow the computer to interact with the external environment, such as users, networks and other systems. |
| Identification and authentication (I&A) | The process of verifying the identity of a user or system and ensuring that they are who they claim to be. |
| IDE (Integrated Development Environment) | A software application that provides a set of tools and features to facilitate the development, testing, debugging and deployment of software programs or applications. |
| Inference engine | A program that uses the knowledge base and the user input to derive conclusions or recommendations. |
| Information asset security | The protection of information resources from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification or destruction. |
| Information security framework | A set of fundamental controls that supports and protects an enterprise’s information assets and enables the implementation of security policies and standards. |
| Information security management | The process of establishing and maintaining an effective information security program that aligns with the business objectives and risk appetite of the organization. |
| Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) | A detailed framework with hands-on information regarding how to achieve successful operational service management of IT, developed by the UK Office of Government Commerce (OGC) in partnership with the IT Service Management Forum. |
| Input/output (I/O) components | Devices that allow the computer to interact with the external environment, such as users, networks and other systems. Examples of input devices are keyboards, mice, scanners and cameras. Examples of output devices are monitors, printers and speakers. |
| Internal control | The policies, procedures, practices and organizational structures designed to provide reasonable assurance that a business process will achieve its objectives and that undesired events will be prevented or detected and corrected. |
| Internal schema | A data schema that describes the physical storage and organization of the data in a database, based on the conceptual schema. |
| Intrusion detection system (IDS) | A device or software that monitors network or system activities for malicious or anomalous behavior and produces reports or alerts to a management station. |
| Intrusion prevention system (IPS) | A device or software that monitors network or system activities for malicious or anomalous behavior and can block or prevent the detected incidents. |
| IS (Information Systems) | The combination of hardware, software, data, people and processes that support the creation, storage, manipulation and communication of information in an organization. |
| IS audit | The formal examination and/or testing of information systems to determine whether they are in compliance with applicable laws, regulations, contracts and/or industry guidelines, and whether they comply with governance criteria and related policies and procedures. |
| IS audit and assurance guidelines | Guidance and additional information on how to comply with the IS audit and assurance standards. |
| IS audit and assurance standards | Mandatory requirements for IS auditing and reporting that inform various audiences of the profession’s expectations concerning the work of practitioners. |
| IS audit and assurance tools and techniques | Examples of processes an IS auditor might follow in an audit engagement. |
| IS auditor | A professional who performs IS audit activities and has the skills and knowledge necessary to perform audit work. |
| ISACA | Information Systems Audit and Control Association, a global association that provides guidance, standards, certification and advocacy for IS audit and assurance professionals. |
| ISO 31000 | A standard that provides guidelines on and a common approach to risk management for organizations. |
| ISO/IEC 20000 | A specification for service management that is aligned with ITIL’s service management framework, consisting of specific requirements for service management improvement and guidance and examples for the application of those requirements. |
| ISO/IEC 27000 series | A set of best practices that provides guidance to organizations implementing and maintaining information security programs. |
| ISO/IEC 38500 | A standard that provides guiding principles for members of governing bodies of organizations on the effective, efficient and acceptable use of IT within an organization. |
| IT (Information Technology) | The use of computers, software, networks, data, telecommunications and other digital technologies to create, store, process, transmit and retrieve information in various forms. |
| IT asset management | A process of identifying, inventorying, managing and protecting IT assets, such as hardware, software, data and information. IT asset management includes assigning owners, custodians, values, locations, security classifications and loss implications to IT assets. |
| IT governance | The leadership and organizational structures and processes that ensure the enterprise sustains and extends strategies and objectives. |
| ITAF | Information Technology Assurance Framework, a comprehensive and good practice-setting reference model that establishes standards, guidelines and tools and techniques for IS audit and assurance. |
| Java | A general-purpose, object-oriented, platform-independent and high-performance programming language that is widely used for developing web, desktop and mobile applications. |
| Job scheduling and production process automation | A process of planning, executing and controlling the batch and online jobs that run on a computer system, using automated job scheduling software. |
| Job scheduling software | System software that sets up daily work schedules and automatically determines which jobs are to be submitted to the system for processing. |
| Key length | The predetermined length of the encryption key, measured in bits. The longer the key, the more difficult it is to break by brute force attacks. |
| Key performance indicator (KPI) | A metric that evaluates the success of an organization or of a particular activity in which it engages. |
| Knowledge base | A collection of facts, rules, heuristics and other information that represents the knowledge of a human expert in a specific domain. |
| LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) | A protocol for accessing and managing information stored in a directory service, such as user names, passwords, email addresses, phone numbers and other attributes. |
| Logon ID and password | The components of a user I&A process, where the logon ID provides individual identification and the password provides individual authentication based on something the user knows. |
| M&A (Mergers and Acquisitions) | The process of combining or transferring the ownership, assets, liabilities and operations of two or more organizations for strategic, financial or operational reasons. |
| Metadata | Data that describe the characteristics and structure of other data, such as data definitions, data types, data relationships and data constraints. |
| Microprocessor | A CPU on a single chip that can be embedded in various devices, such as personal computers, smartphones, tablets and appliances. |
| Motherboard | The main circuit board of a computer that connects and supports the CPU, memory, storage devices and other components. |
| MTS (Microsoft Transaction Server) | A software component that provides transaction processing, object pooling, security, load balancing and other services for developing and deploying distributed applications on Windows platforms. |
| Multi-core processor | A CPU that contains multiple processing units or cores on a single chip, which can execute multiple instructions simultaneously. |
| Multi-processor | A computer system that has more than one CPU, which can work in parallel to increase the processing speed and performance. |
| Network database model | A database model that organizes data in a graph-like structure, using owner-member relationships. |
| OBS (Object Breakdown Structure) | A hierarchical representation of the individual components of the solution and their relationships to each other in a project. |
| Open Information Security Management Maturity Model (O-ISM3) | A process-based ISM maturity model for security. |
| Password syntax rules | The rules that define the format and characteristics of a valid password, such as length, complexity and expiration. |
| Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) | An industry standard for organizations that process payment cards (e.g., debit cards and credit cards) that specifies the requirements for securing cardholder data and the network environment. |
| Permanent storage devices | Devices that store data and programs permanently, such as hard disk drives and solid-state drives. |
| PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) | A project management technique that uses three different estimates of each activity duration and applies a mathematical formula to determine the expected completion time and variance of the project. |
| PID (Project Initiation Document) | A document that defines the purpose, scope, objectives, deliverables, risks, assumptions, constraints, stakeholders, governance and resources of a project, and serves as the basis for its management and assessment. |
| PMO (Project Management Office) | A centralized unit within an organization that oversees and coordinates the management of projects, programs and portfolios, and provides guidance, standards, methodologies, tools and best practices. |
| Policies | Statements of management intent, supporting the goals and principles of information security in line with the business strategy and objectives. |
| PRD (Project Request Document) | A document that outlines the business need, requirements, benefits, feasibility, risks and estimated costs of a proposed project, and serves as the input for the project initiation process. |
| Procedures | Step-by-step instructions that detail the exact manner in which a task or process is to be performed. |
| QA (Quality Assurance) | The process of ensuring that the quality standards and requirements of a project are met and that the project deliverables conform to the specifications and expectations of the stakeholders. |
| Radio frequency identification (RFID) | A technology that uses radio waves to identify tagged objects within a limited range. |
| Random access memory (RAM) | A type of volatile memory that stores data and instructions that are currently being used by the CPU. |
| Read-only memory (ROM) | A type of non-volatile memory that stores data and instructions that are essential for the basic operation of a computer, such as the boot process. |
| Relational database model | A database model that organizes data in tables, using rows and columns. |
| Return on investment (ROI) | A measure of the profitability or efficiency of an investment, calculated as the ratio of the net benefit (benefit minus cost) to the cost of the investment. |
| Risk | The combination of the probability of an event and its consequence. |
| Risk analysis | The process of comprehending the nature of risk and determining the level of risk. |
| Risk appetite | The amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to pursue or retain. |
| Risk assessment | The process of identifying and evaluating the potential impact and likelihood of threats and vulnerabilities to the organization’s assets and processes. |
| Risk evaluation | The process of comparing the results of risk analysis with risk criteria to determine whether the risk and/or its magnitude is acceptable or tolerable. |
| Risk identification | The process of finding, recognizing and describing risks. |
| Risk management | The coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with regard to risk. |
| Risk register | A record of information about identified risks. |
| Risk tolerance | The organization’s or stakeholder’s readiness to bear the risk after risk treatment in order to achieve its objectives. |
| Risk treatment | The process of selecting and implementing measures to modify risk. |
| Sampling | The process of selecting a subset of items from a population for the purpose of making inferences about the population. |
| SD/MMC (Secure Digital/MultiMedia Card) | A type of flash memory card that is used for storing data in portable devices, such as digital cameras, mobile phones, music players and laptops. |
| SDLC (System Development Life Cycle) | A structured and systematic approach to developing, implementing, maintaining and disposing of information systems and related components. |
| Security administrator | A person responsible for the security of the shared data stored on database systems, implementing and monitoring security policies and controls, and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. |
| SME (Subject Matter Expert) | A person who has extensive knowledge and experience in a specific domain or topic, and provides guidance, input, feedback or validation to a project team. |
| Social media | A collection of web-based platforms and applications that enable users to create and share content and interact with other users and communities online. |
| Solid-state drive (SSD) | A type of permanent storage device that uses flash memory to store data, without any moving parts. |
| Standards | Documents that establish specifications and procedures designed to ensure the reliability of the materials, products, methods and/or services people use every day. |
| Substantive testing | The process of verifying the accuracy and completeness of data and transactions through analytical or detailed tests. |
| Symmetric encryption | A type of encryption that uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, also known as secret key encryption or single key encryption. |
| Systems administrator | A person responsible for maintaining major multiuser computer systems, including local area networks (LANs), wireless local area networks (WLANs), wide area networks (WANs), virtual machine/server/network environments, personal area networks (PANs), storage area networks (SANs), intranets and extranets, and mid-range and mainframe systems. |
| Technology components | Hardware, software, network and data resources that enable the processing and delivery of information in an organization. |
| Token device | A physical object that a user possesses and uses to authenticate their identity, such as a smart card, a USB key or a mobile device app, that generates a one-time password or a session password. |
| Types of computers | Computers can be categorized according to their processing power, size and architecture, such as supercomputers, mainframes, high-end/midrange servers, personal computers, thin client computers, laptop computers, smartphones, tablets and other handheld devices. |
| Universal serial bus (USB) | A standard interface that connects peripheral devices, such as keyboards, mice, printers, cameras, flash drives and external hard drives, to a computer or other host device. |
| USB (Universal Serial Bus) | A serial bus standard that connects devices to a host computer, allowing data transfer, power supply and plug-and-play functionality. |
| Variable sampling | A sampling technique used to estimate the monetary value or some other unit of measure of a population, such as the total error amount or the average transaction value. |
| WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) | A hierarchical decomposition of the work to be performed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. |
| WP (Work Package) | A defined and manageable unit of work within the WBS that has a specific scope, schedule, budget and assigned resources. |