Table of Contents
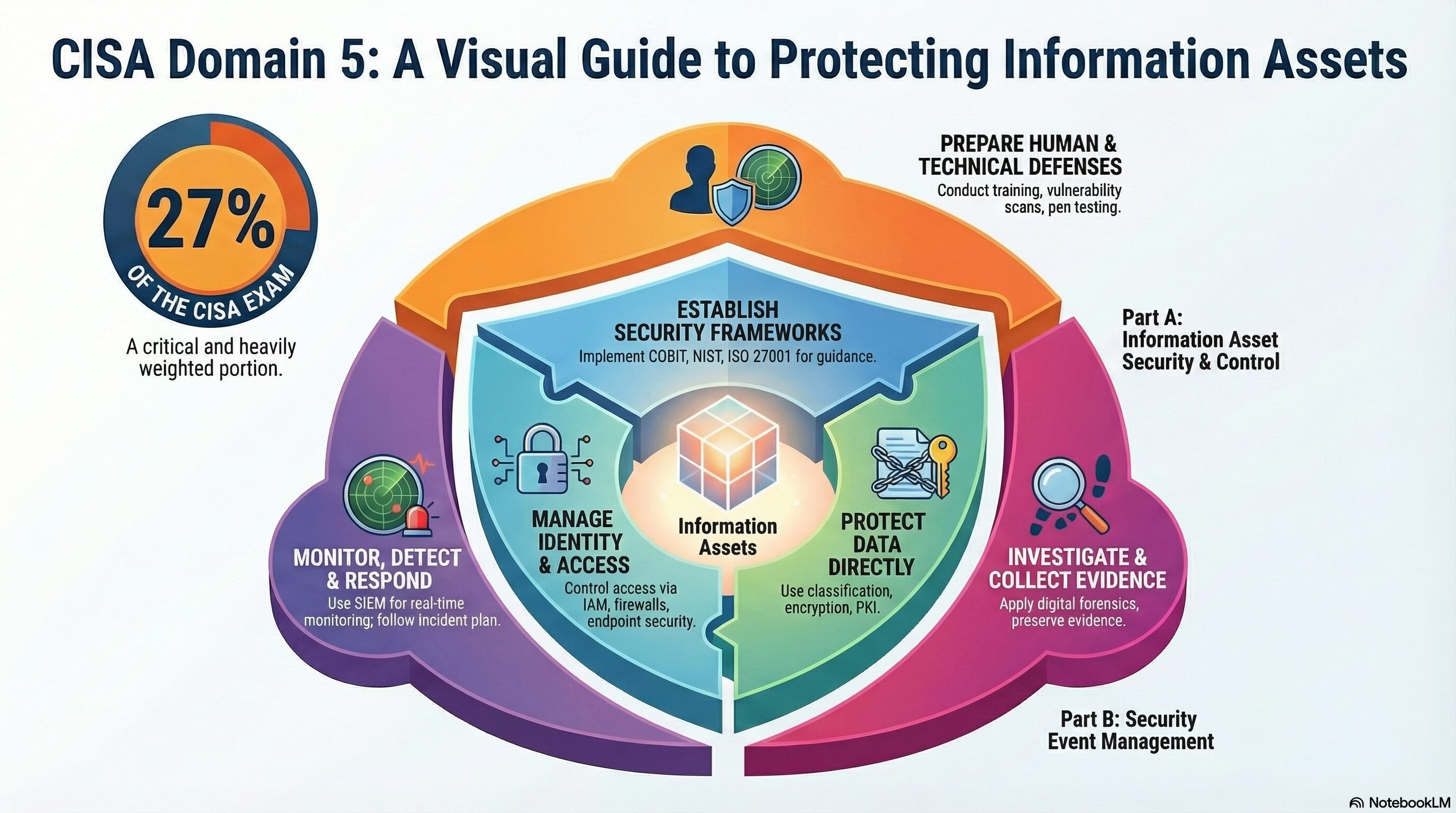
The Domain 5: Protection of Information Assets of CISA exam holds a total weightage of 27% in the exam.
Domain 5: Protection of Information Assets of the CISA exam focuses on safeguarding information assets through security controls and proactive measures. Here’s a summary of the key objectives within Part A and Part B:
Part A: Information Asset Security and Control
- Information Asset Security Frameworks, Standards, and Guidelines: This objective covers frameworks like COBIT, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and ISO 27001, helping you understand how to implement best practices for information security.
- Privacy Principles: Learn about data privacy principles such as notice, choice, access, and security, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Physical Access and Environmental Controls: Understand physical security measures like access control systems, surveillance, and environmental monitoring to protect hardware and data from unauthorized access and physical threats.
- Identity and Access Management: Master various techniques like authentication, authorization, and RBAC to manage user access to sensitive information and systems.
- Network and End-point Security: This covers network security controls like firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and endpoint security solutions like antivirus and anti-malware to protect against cyberattacks.
- Data Classification: Learn how to classify information based on its sensitivity and criticality, allowing for appropriate security controls and protection levels.
- Data Encryption and Encryption-related Techniques: Understand various encryption algorithms and key management practices to protect data at rest, in transit, and in use.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Grasp the concepts of certificates, digital signatures, and PKI to secure communication and authenticate identities.
- Web-based Communication Technologies: Understand the security considerations for web applications, email, and cloud services to ensure secure communication and data transmission.
- Virtualized Environments: Learn about security challenges and controls specific to virtualized environments like servers and desktops.
- Mobile, Wireless, and Internet-of-Things (IoT) Devices: Understand the unique security risks and controls associated with mobile devices, wireless networks, and IoT devices.
Part B: Security Event Management
- Security Awareness Training and Programs: Learn how to develop and implement effective security awareness programs to educate users and foster a culture of security within an organization.
- Information System Attack Methods and Techniques: Gain knowledge about common cyberattacks and attack vectors to better understand vulnerabilities and prepare defenses.
- Security Testing Tools and Techniques: Learn about various security testing tools and techniques like vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and code reviews to identify and address security weaknesses.
- Security Monitoring Tools and Techniques: Understand how to use security information and event management (SIEM) systems and other monitoring tools to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time.
- Incident Response Management: This objective covers the essential steps to handle security incidents effectively. You’ll learn about incident response plans, investigation procedures, containment and eradication techniques, communication protocols, and recovery processes. Understanding these steps will equip you to minimize damage, preserve evidence, and restore normal operations efficiently in the event of a security breach.
- Evidence Collection and Forensics: This objective delves into the crucial aspects of evidence collection and forensics in the aftermath of a security incident. You’ll learn about proper methods for preserving and collecting digital evidence, including logs, files, network traces, and other relevant data. Additionally, you’ll gain insights into forensic analysis techniques used to reconstruct the incident timeline, identify the attackers, and gather evidence for potential legal proceedings.
This summary provides a high-level overview of the key objectives. Remember to delve deeper into each topic using official CISA study materials and practice questions to fully grasp the concepts and excel in the exam.
Unique Terms and Definitions from Domain 5: Protection of Information Assets
- Antivirus software: A program that can prevent, detect and remove malware infections on a computer system.
- Information asset security: The protection of information resources from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification or destruction.
- Confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA): The three key objectives of information security, also known as the CIA triad.
- Information security management: The process of establishing and maintaining an effective information security program that aligns with the business objectives and risk appetite of the organization.
- Information security framework: A set of fundamental controls that supports and protects an enterprise’s information assets and enables the implementation of security policies and standards.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): An industry standard for organizations that process payment cards (e.g., debit cards and credit cards) that specifies the requirements for securing cardholder data and the network environment.
- Control framework: A collection of best practices, guidelines and methodologies for designing, implementing and assessing controls in an organization.
- Return on investment (ROI): A measure of the profitability or efficiency of an investment, calculated as the ratio of the net benefit (benefit minus cost) to the cost of the investment.
- Risk assessment: A process of identifying, analyzing and evaluating the risks that an organization faces and determining the appropriate risk responses and controls.
- Security administrator: A person who is responsible for providing adequate physical and logical security for information systems, programs, data and equipment.
- Data owner: A person who is accountable for the security and use of a specific set of information assets, such as data or applications.
- Data custodian: A person who is responsible for storing and safeguarding the data and providing access to authorized users.
- Data user: A person who accesses and uses the data for legitimate business purposes.
- Card key: A physical access control technique that uses a plastic card with a magnetic strip or a chip containing encoded data to provide access to restricted or secure locations.
- Biometric access control: A logical access control technique that uses a person’s unique physical or behavioral characteristics, such as fingerprint, iris, voice or signature, to verify their identity.
- Identification and authentication (I&A): The process of verifying the identity of a user or system and ensuring that they are who they claim to be.
- Logon ID and password: The components of a user I&A process, where the logon ID provides individual identification and the password provides individual authentication based on something the user knows.
- Password syntax rules: The rules that define the format and characteristics of a valid password, such as length, complexity and expiration.
- Token device: A physical object that a user possesses and uses to authenticate their identity, such as a smart card, a USB key or a mobile device app, that generates a one-time password or a session password.
- Encryption: The process of converting a plaintext message into a ciphertext that cannot be understood without converting it back via decryption using a key.
- Encryption algorithm: A mathematical function that encrypts and decrypts data using a key.
- Encryption key: A piece of information that is used by the encryption algorithm to make the encryption or decryption process unique.
- Key length: The predetermined length of the encryption key, measured in bits. The longer the key, the more difficult it is to break by brute force attacks.
- Symmetric encryption: A type of encryption that uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, also known as secret key encryption or single key encryption.
- Asymmetric encryption: A type of encryption that uses a pair of keys, one for encryption and one for decryption, also known as public key encryption or dual key encryption.
- Digital signature: A technique that uses asymmetric encryption to verify the authenticity and integrity of a message or document by applying the sender’s private key to a digest of the message or document.
- Digital envelope: A technique that combines symmetric and asymmetric encryption to securely transmit data and a secret key, by encrypting the data with the secret key and then encrypting the secret key with the recipient’s public key.
- Firewall: A device or software that monitors and controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules, acting as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks.
- Intrusion detection system (IDS): A device or software that monitors network or system activities for malicious or anomalous behavior and produces reports or alerts to a management station.
- Intrusion prevention system (IPS): A device or software that monitors network or system activities for malicious or anomalous behavior and can block or prevent the detected incidents.
- Honeypot: A decoy system or network that is designed to attract and trap attackers, diverting them from the real targets and collecting information about their activities and techniques.
- Social media: A collection of web-based platforms and applications that enable users to create and share content and interact with other users and communities online.
- Cloud computing: A model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
- Cloud service models: The three types of services offered by cloud providers, namely software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
- Cloud deployment models: The four types of cloud environments, namely public cloud, private cloud, community cloud and hybrid cloud.
Multiple Choice Questions quiz
|
Flashcard quiz
|