Table of Contents
The Domain 3: Information Systems Acquisition, Development & Implementation of CISA exam holds a total weightage of 12% in the exam.
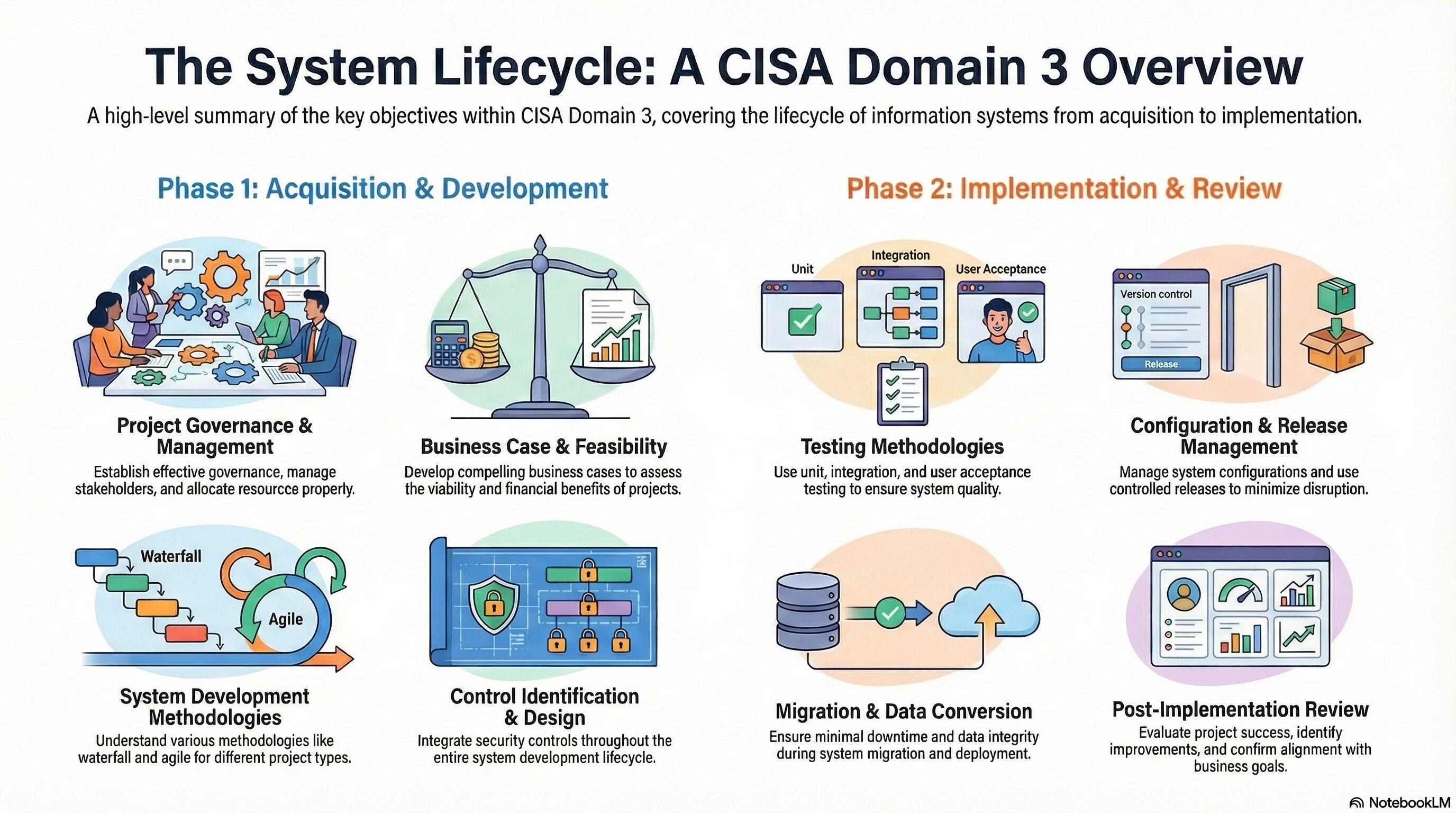
Domain 3: Information Systems Acquisition, Development & Implementation of the CISA exam focuses on the lifecycle of information systems, from conceptualization and acquisition to development, implementation, and post-implementation review. Here’s a summary of the key objectives within Part A and Part B:
Part A: Information Systems Acquisition and Development
- Project Governance and Management: Understand the principles and best practices for effective project governance, including stakeholder management, risk management, and resource allocation.
- Business Case and Feasibility Analysis: Learn how to develop compelling business cases and conduct feasibility studies to assess the viability and financial benefits of proposed information system projects.
- System Development Methodologies: Understand different system development methodologies (e.g., waterfall, agile) and their suitability for various project types and contexts.
- Control Identification and Design: Grasp the importance of integrating security controls throughout the system development lifecycle and learn techniques for identifying and designing appropriate controls.
Part B: Information Systems Implementation
- Testing Methodologies: Understand various testing methodologies (e.g., unit testing, integration testing, user acceptance testing) and their role in ensuring system quality and functionality.
- Configuration and Release Management: Learn about managing system configurations and implementing controlled release processes to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
- System Migration, Infrastructure Deployment and Data Conversion: Understand the processes and best practices for migrating systems, deploying new infrastructure, and converting data to the new system, ensuring minimal downtime and data integrity.
- Post-implementation Review: Learn how to conduct post-implementation reviews to evaluate the success of the project, identify areas for improvement, and ensure alignment with project goals and business objectives.
Unique Terms and Definitions from Domain 3: Information Systems Acquisition, Development & Implementation
- EDI (Electronic Data Interchange): The exchange of structured data between computer systems according to agreed standards.
- IS (Information Systems): The combination of hardware, software, data, people and processes that support the creation, storage, manipulation and communication of information in an organization.
- SDLC (System Development Life Cycle): A structured and systematic approach to developing, implementing, maintaining and disposing of information systems and related components.
- CSF (Critical Success Factor): A factor that is essential for achieving a desired outcome or objective of a project, program or organization.
- OBS (Object Breakdown Structure): A hierarchical representation of the individual components of the solution and their relationships to each other in a project.
- WBS (Work Breakdown Structure): A hierarchical decomposition of the work to be performed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables.
- WP (Work Package): A defined and manageable unit of work within the WBS that has a specific scope, schedule, budget and assigned resources.
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique): A project management technique that uses three different estimates of each activity duration and applies a mathematical formula to determine the expected completion time and variance of the project.
- CPM (Critical Path Method): A project management technique that identifies the sequence of activities that produces the longest path through a project and determines the shortest possible completion time of the project.
- PMO (Project Management Office): A centralized unit within an organization that oversees and coordinates the management of projects, programs and portfolios, and provides guidance, standards, methodologies, tools and best practices.
- PID (Project Initiation Document): A document that defines the purpose, scope, objectives, deliverables, risks, assumptions, constraints, stakeholders, governance and resources of a project, and serves as the basis for its management and assessment.
- PRD (Project Request Document): A document that outlines the business need, requirements, benefits, feasibility, risks and estimated costs of a proposed project, and serves as the input for the project initiation process.
- QA (Quality Assurance): The process of ensuring that the quality standards and requirements of a project are met and that the project deliverables conform to the specifications and expectations of the stakeholders.
- SME (Subject Matter Expert): A person who has extensive knowledge and experience in a specific domain or topic, and provides guidance, input, feedback or validation to a project team.
- ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram): A graphical representation of a system’s data and how they interrelate, using entities, attributes, keys and relationships. An ERD can be used as a logical data model or a physical data model.
- EAL (Evaluation Assurance Level): A numerical rating that indicates the level of confidence in the security functionality and assurance of an IT product or system, based on a standardized criteria and evaluation process.
- IDE (Integrated Development Environment): A software application that provides a set of tools and features to facilitate the development, testing, debugging and deployment of software programs or applications.
- 4GL (Fourth-generation Language): A high-level, nonprocedural, portable and user-friendly programming language that allows developers to focus on the business functionality and logic rather than the technical details of the system.
- CASE (Computer-aided Software Engineering): The use of automated tools to support the software development process, such as requirements analysis, design, coding, testing, documentation and maintenance.
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): A large-scale, integrated software system that supports the core business processes and functions of an organization, such as accounting, finance, human resources, manufacturing, sales and marketing.
- M&A (Mergers and Acquisitions): The process of combining or transferring the ownership, assets, liabilities and operations of two or more organizations for strategic, financial or operational reasons.
- BPR (Business Process Reengineering): The radical redesign and improvement of the existing business processes, workflows and systems of an organization to achieve significant gains in performance, quality, customer satisfaction and profitability.
- IT (Information Technology): The use of computers, software, networks, data, telecommunications and other digital technologies to create, store, process, transmit and retrieve information in various forms.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The main component of a computer system that executes the instructions of a program and performs the arithmetic and logical operations.
- LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol): A protocol for accessing and managing information stored in a directory service, such as user names, passwords, email addresses, phone numbers and other attributes.
- MTS (Microsoft Transaction Server): A software component that provides transaction processing, object pooling, security, load balancing and other services for developing and deploying distributed applications on Windows platforms.
- EJB (Enterprise Java Beans): A server-side component model for developing and deploying distributed, scalable, secure and transactional business applications on Java platforms.
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): A standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications, using tags, elements and attributes to define the structure and content of the document.
- ActiveX: A software framework and technology that allows components to interact and share information across different applications and platforms, such as web browsers, Microsoft Office and Windows OS.
- Java: A general-purpose, object-oriented, platform-independent and high-performance programming language that is widely used for developing web, desktop and mobile applications.
- COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language): A procedural, imperative and compiled programming language that is designed for business applications and runs on a variety of platforms, such as mainframes, minicomputers and microcomputers.
- DFD (Data Flow Diagram): A graphical representation of the flow of data and the processing steps of a system or a process, using symbols such as circles, arrows, rectangles and parallel lines.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus): A standard interface that connects peripheral devices, such as keyboards, mice, printers, cameras, flash drives and external hard drives, to a computer or other host device.
- SD/MMC (Secure Digital/MultiMedia Card): A type of flash memory card that is used for storing data in portable devices, such as digital cameras, mobile phones, music players and laptops.
- IS auditor: A professional who performs independent and objective assessments of the effectiveness, efficiency, reliability, security and compliance of information systems and related processes, controls and governance.
Multiple Choice Questions quiz
|
Flashcard quiz
|